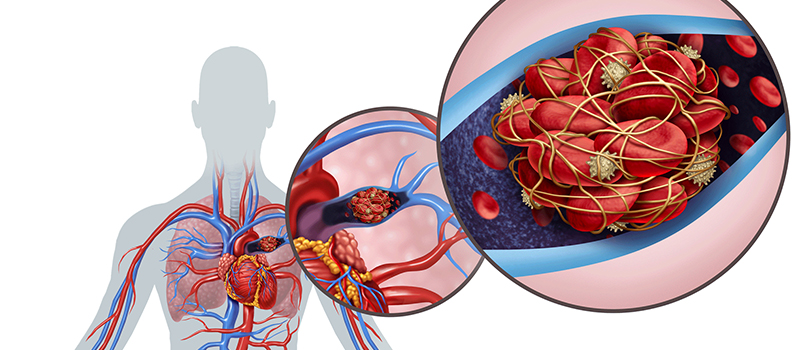
Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism is when one or more clots block the main artery leading to the lungs. It can be fatal if untreated, but medication is often treatable. This article will explain pulmonary embolism and how it’s diagnosed and treated.
What is pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of the main artery in the lung. This can be caused by several factors, including blood clots that enters the lungs from elsewhere in the body.
When these clots or other materials become lodged in an artery and cause it to close off, blood flow through that part of your body is cut off, resulting in severe injury or death. If a clot travels through veins deep within your leg to reach your lungs and block an artery there, it’s referred to as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT is more common than PE; however, both conditions are severe and require immediate treatment by healthcare professionals.
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism
Shortness of breath: You may experience shortness of breath and a sense of pressure in your chest.
Coughing up blood: This sign that the pulmonary embolism has caused a pulmonary infarction or blockage in the lung tissue.
Chest pain: You might feel chest pain when you inhale and exhale, especially if the affected area is your heart or lungs.
Fainting: An episode of fainting that lasts less than five minutes can be a sign of pulmonary embolism if it happens shortly after exercise or sex, according to experts on pulmonary embolisms. These episodes are called”syncope” (SINK-oh-pee). It’s important to note that people with previous episodes are prone to more syncope each year because their bodies become more sensitive to low oxygen levels during exertion.
Sweating: Your skin may feel clammy and cool during an episode associated with this condition; however, there should be no fever unless another infection coexists along with the PE
Causes of pulmonary embolism
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Pregnancy
- Prolonged bed rest
- Cancer, including lung cancer and lymphoma
- Surgery, especially orthopedic surgeries like hip replacement that may require an indwelling catheter or prolonged immobility in the hospital
- Trauma to the pelvis or lower extremities that causes damage to the blood vessels there (e.g., fracture of a lower limb)

Treatment options for pulmonary embolism
Treatment options for pulmonary embolism may include:
Blood thinners (anticoagulants): These medications are given to prevent the formation of new blood clots. They include warfarin or low-molecular-weight heparins, such as enoxaparin (Lovenox) and dalteparin (Fragmin).
Thrombolytics: These drugs break up existing blood clots. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA) is the only approved thrombolytic drug for PE treatment but has a narrow window of efficacy and requires IV infusion within three hours after symptoms begin. Other intravenous options include urokinase and streptokinase; however, these drugs have been replaced mainly by rtPA due to their superior safety profile and broader therapeutic time window for administration.
Embolectomy: Pulmonary embolectomy removes clots using an endoscope inserted into an artery in your leg or arm. Balloon pulmonary embolectomy uses a small device placed inside an artery in the groin area to push or suck out clot material; surgery with either mechanical device placement or manual removal of acute PEs.
Prognosis
The prognosis for pulmonary embolism depends on the severity of symptoms and whether you have another underlying condition that makes you more likely to develop pulmonary embolism.
Request a Consultation
Pulmonary embolism can be severe, but it is not always fatal. If you are suffering from symptoms of pulmonary embolism, it is vital that you seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Let the treatment specialists at Washington Vascular Specialist treat your pulmonary embolism symptoms with our state-of-the-art technology. Contact us to book an appointment.