Pulmonary Embolism
The human heart pumps oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body. However, it is the lungs that are responsible for supplying the blood with oxygen.
The pulmonary artery helps deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it is supplied with rich air. From the lungs, the blood is pumped back to the heart before being supplied all over the body.
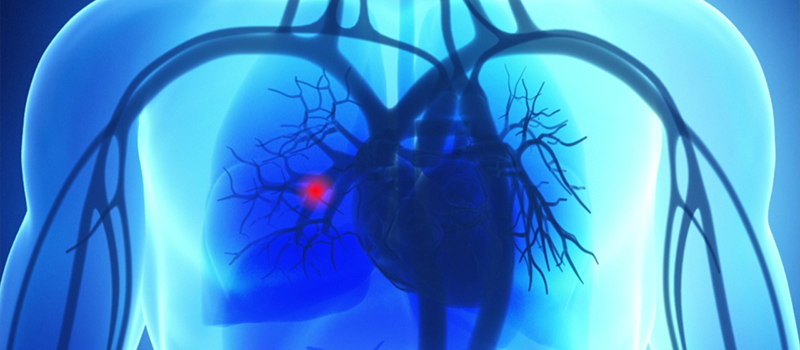
Pulmonary embolism is a condition where blood clots (deep vein thrombosis) get into one of the arteries between the heart and the lung. This blood clot tampers with the normal flow of blood. When left untreated, pulmonary embolism can lead to severe health conditions such as a septic embolism.
What are the risk factors associated with pulmonary embolism?
As established above, a pulmonary embolism occurs when blood clots end up wedged into an artery in the lungs. However, not all cases of pulmonary embolism are caused by blood clots. In some cases, other foreign material may find itself lodged in the pulmonary arteries. These foreign materials could be air bubbles, fat from the bone marrow of a broken bone, or even part of a tumor.
Some of the most prevalent risk factors contributing to pulmonary embolism include the following;
1. Medical treatments and conditions
Some treatments and medical conditions can significantly contribute to pulmonary embolism. Additionally, some of these conditions are familiar. If you or someone close to you has experienced any of the following, they should also get checked for pulmonary embolism symptoms as soon as possible.
- Cancers – Cancers that affect the brain, lungs, kidneys, pancreas, and ovary can increase the chance of suffering from a pulmonary embolism. Additionally, cancer treatments such as chemotherapy can also increase the risk levels. The analysis also shows women exposed to breast cancer and take either raloxifene or tamoxifen are at a higher chance of experiencing blood clots.
- Heart diseases – Cardiovascular illnesses such as heart failure increase the likelihood of blood clot formation.
- Surgeries – Surgery and surgical intervention are amongst the leading causes of blood clots that materialize to pulmonary embolism.
2. Prolonged immobility
Blood clots are likely to appear during or after long periods of rest and inactivity. Sitting in the same position for long or being confined to bed rest can lead to blood clots and eventually pulmonary embolism.
Other risk factors include:
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Supplemental estrogen
What are the leading symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
The symptoms can often vary from one patient to another. Other factors include the size of the blood clot, condition progression, and underlying heart and lung conditions.
Some of the common noticeable pulmonary embolism symptoms are:
- Fever
- Excess sweating
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Irregular or rapid heartbeat
- Discolored or clammy skin (cyanosis)
- Leg swelling and pain
When should you consult a doctor?
Pulmonary embolisms can quickly turn life-threatening. If you are experiencing sudden but unexplained shortness of breath, cough, or chest pain, you should soon seek medical intervention. Get in touch with the leading experts from Washington Vascular Specialists to help you deal with all your pulmonary embolism issues.