Veins and arteries ship oxygen back and forth between the heart and the lungs through blood. If you have an arteriovenous malformation, this process becomes impaired. That means that your cells and tissues may not get enough oxygen. Also, the affected AVM blood vessels may rupture. Read on to find out what AVM is, the symptoms to watch out for, and treatment options.
What are Arteriovenous Malformations (AVM)?
AVMs are a type of abnormal connection between arteries and veins in your body. It's like a tangled mess of blood vessels that impact blood flow and oxygenation. The blood vessels connect to other vessels without passing through normal capillaries. This abnormal connection results in high arterial pressure and slow venous drainage. These factors can cause bleeding, including spontaneous intracellular hemorrhage (ICH).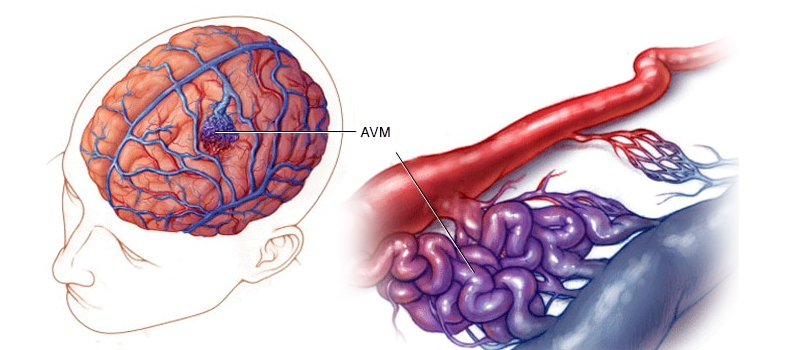
Symptoms
The symptoms you may experience due to AVM vary depending on its location. Some people may not experience symptoms, while others may have more severe ones. Common symptoms of AVMs include:
- Headaches ranging from mild to severe
- Weakness or numbness in the arms or legs
- Double vision, blurred images, or even complete loss of sight.
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing
- Back pain
- Hallucinations
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, have a family history of AVM, or have been diagnosed with one, follow up with a medic for check-ups and monitoring.
Causes
So, what causes AVMs? Well, experts don't know. Some researchers believe they are a result of abnormal development in the womb. Some risk factors for AVMs include:
- Family history of the condition.
- Certain genetic disorders, such as Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing an AVM involves a combination of imaging tests and physical examinations. Your doctor may perform a neurological exam to assess the following:
- Your reflexes
- coordination
- Other neurological functions
They may also take a medical history and ask about any symptoms you’re experiencing.
To confirm if you have an AVM, your doctor will likely recommend an imaging test like an MRI or CT scan. These tests can visualize abnormal vessels and determine the location of the AVM. In some cases, your medic may recommend an angiography. This involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels to get a clearer picture of the AVM. Magnetic resonance angiography is another diagnostic option. It reveals the pattern and speed of blood flow in the blood vessels.
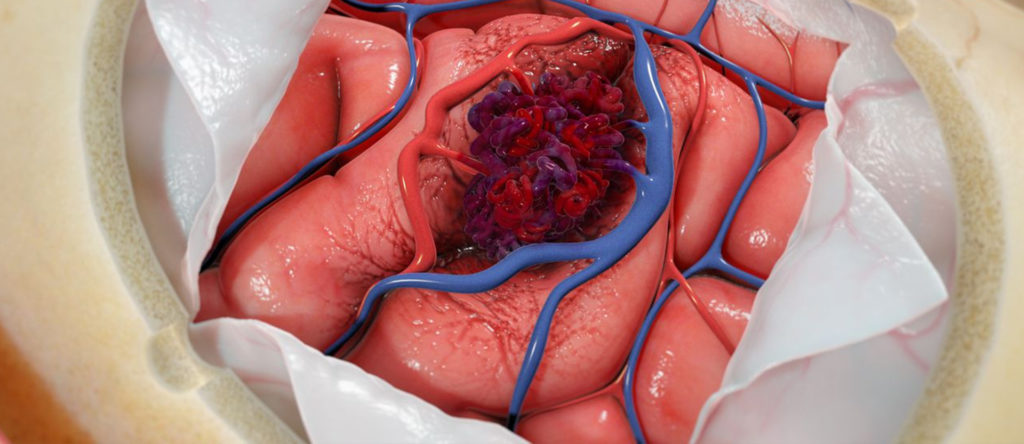
Treatment Options for Arteriovenous Malformations (AVM)
Treatment for AVMs depends on the size and location of the malformation. The severity of symptoms may also affect the treatment.
Treatment options include mediation and surgery. Surgery options include embolization,v radiation therapy and endovascular coiling procedures. Doctors often recommend surgery if the AVM is causing complications such as bleeding orb doesn’;t respond to medication. Surgery can help to remove the entire without causing severe damage to the surrounding tissues, nerves or blood vessels. Your doctor will recommend the best treatment option based on the size and location of your AVM, your age and overall health, and the extent of your symptoms.
Conclusion
Arteriovenous malformations (AVM) can be a serious health concern if left untreated. If you experience any symptoms of AVMs, we recommend consulting a specialist. Contact Washington Vascular Specialists today to schedule a consultation and learn more about how we can help diagnose and treat AVMs. We are conveniently located in Takoma Park, Largo, Frederick, Baltimore, and Gaithersburg, Maryland.