Carotid Artery Disease Management And Treatment
Understanding the causation and progression process of a disease gives you the best chance to combat it. Carotid artery disease is a serious vascular illness that can affect anyone.
This vascular condition can greatly affect your life quality and health. What exactly is carotid artery disease, and who is at risk of developing vascular illness? More importantly, what are the early symptoms of this condition, and what can you do about it? Read on to learn more about the management and treatment of carotid artery disease (CAD).
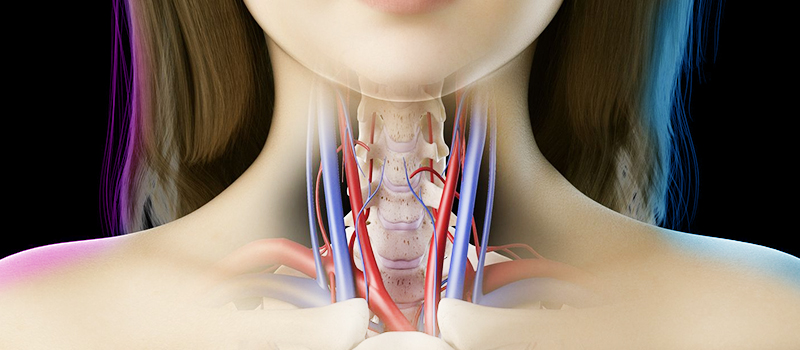
What is carotid artery disease?
CAD is a vascular condition that develops when foreign material is lodged in the carotid arteries. The foreign material could be fatty deposits, plaque, and other items not commonly found in the bloodstream.
The carotid arteries are tasked with moving oxygenated blood from the heart to the head and brain. Blockage of these vital arteries can lead to severe health complications. For example, blocked or narrowed carotid arteries can significantly increase the risk of suffering from a stroke attack.
The foreign material accumulates gradually over time. If you’re not keen on your health, you may realize the condition after it’s progressed to its latter stages. This points to the importance of regular vascular checkups.
The primary cause of carotid artery disease is atherosclerosis. In these cases, the fatty deposits form a layer that thickens over time. Consequently, this lowers the amount of blood flowing to the brain. If the condition is not addressed in time, it can completely cut off the supply of oxygenated blood to the brain.
Certain favors have been identified to increase the chances of developing CAD. Some of the common associative risk factors include;
- High cholesterol
- Tobacco use
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Lack of exercise
- Age
- Genetic factors
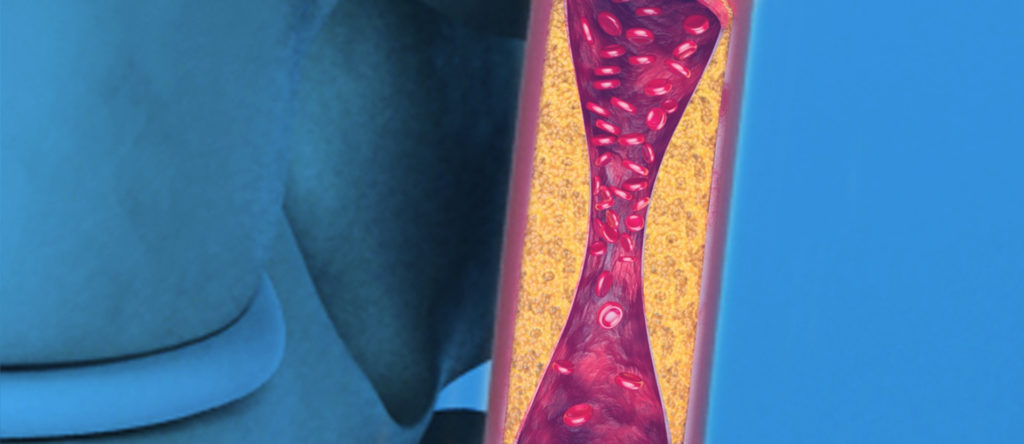
Symptoms of carotid artery disease
CAD can develop for a long time with little to no symptoms. In some cases, a stroke attack is often the first notable sign of the condition. A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is another sign usually associated with CAD.
TIA occurs when one part of the brain is briefly deprived of oxygen-rich blood. The symptoms of TIA are usually temporary and can completely disappear in less than a day. Some of the signs of TIA include the following;
- Arm or leg weakness on one side of the body
- Reduced coordination
- Confusion, dizziness, headaches, and fainting
- Temporary blurred vision
- Numbness in the face, leg, or arm
CAD treatment and management
Doctors can use various management and treatment methods depending on numerous factors. These include the client’s age, health status, medical history, and preference.
Additionally, vascular professionals use a combination of lifestyle adjustments and medication to manage and treat the condition. Some of the lifestyle changes you’ll be advised to follow include lowering your blood sugar, tobacco use, cholesterol, and blood pressure. You’ll also have to include regular exercise in your life.
When it comes to medication, doctors can prescribe cholesterol-lowering medicine, blood pressure-lowering medicine, and antiplatelets. In cases of extreme progression, doctors can also use surgical intervention.
Washington Vascular Specialists are the leading management and treatment center for all matters relating to carotid artery disease. Consult a vascular expert today and stop the progression of this serious vascular illness.