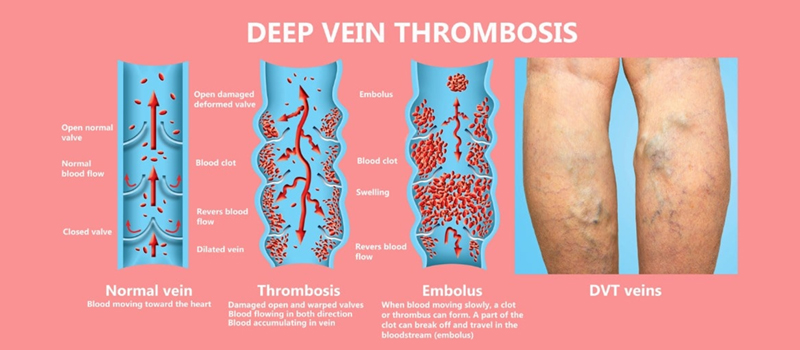
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Could that swelling on your foot or ankle be Deep Vein Thrombosis? Early diagnosis and treatment may help reduce the risk of a pulmonary embolism and prevent future clots. Call Washington Vascular Specialists at 301-891-2500.
DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) is caused by blood clots forming in the legs or one or more deep veins in your body. The ischemic after-effects can cause leg pain or swelling, although DVT may
also be asymptomatic.
A serious condition
This condition is highly dangerous because blood clots can break free in your veins, travel through your bloodstream and clog your lungs (pulmonary embolism). DVT, however, does not automatically lead to pulmonary embolism.
Deep vein thrombosis can occur if your blood clots is differently due to certain medical conditions.
It can also occur due to long periods of immobility, like following a surgery or accident.
DVT symptoms
DVT clots typically form in the legs or thighs; however, they may form anywhere else in your body. Thromboembolism, post-thrombotic syndrome, and postphlebitic are all terms associated with this condition.
Around half of the people with DVT experience symptoms. Symptoms can include:
• One-sided swelling of your foot, ankle, or leg
• Acute pain in the affected foot starting in your calf.
• Unusual pain in your feet and ankles
• The affected area feels warmer compared to surrounding skin
• Pale or bluish skin over the affected area
Call a doctor
If you experience symptoms of DVT, please contact your physician. However, in most cases, people aren’t aware of having DVT until they’ve been diagnosed with pulmonary embolisms (blood clots in the lungs).
A pulmonary embolism (PE) can have catastrophic consequences. Seek emergency medical attention.
A pulmonary embolism has the following symptoms:
• Breathlessness
• Pain in the chest
• Lightheadedness or dizziness, or feeling faint
• Elevated heart rate
• Rapid breathing
DVT Causes
DVT can be caused by anything that interferes with blood flow or accelerates clotting. Infection
or injury to a vein can also result in DVT.
DVT Risk factors
Many factors can increase your risk of DVT. The DVT Risk factors include:
• Old age
• Pregnancy
• Prolonged sitting
• Injury
• Surgery
• Heart failure
• Genetics
DVT Treatment
If you suspect DVT or PE, consult your doctor right away. A vascular health specialist can examine your symptoms.

DVT treatment options include:
Medication
Blood thinners such as heparin, warfarin, enoxaparin, and fondaparinux can prevent the formation or expansion of clots.
Compression stockings
You may be less likely to develop clots if you wear compression stockings.
Filters
If you cannot take blood thinners, a filter might need to be placed inside your large abdominal vein. In this form of treatment, clots are stopped from entering the lungs, which helps prevent
pulmonary embolisms.
DVT surgery
DVT clots in the arm or leg may be removed by surgery. Usually, the surgery, surgical thrombectomy, is reserved for removing clots that have caused serious issues, such as tissue
damage.
To carry out the procedure, the specialist will make an incision into the affected blood vessel.
Upon finding the clot, they’ll remove it. After that, they’ll repair the vessel and the affected tissue.
The risks of this procedure include infection, blood vessel damage, and excessive bleeding.
WASHINGTON Vascular Specialists provide comprehensive vascular care that is comfortable, affordable, and individualized to each patient’s needs. Leading-edge therapeutic innovations,
doctor-patient collaboration, and minimally invasive solutions are the building blocks of our care.
For comprehensive care and treatment against Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), call us at 301-891-
2500.